How to Add Identity Context to RADIUS Auth for ZTNA
Impersonating machines in the digital age is becoming very convenient. Hackers constantly employ these techniques to penetrate the defenses of business networks. Once inside their trusted gadgets, they can travel laterally across systems to steal encrypted data.
Here’s a recent cyberattack reported by the Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC), sanctioning several individuals and entities involved in the malicious act. It is pretty apparent that to counter these advanced cyberattacks, you must upgrade your network security infrastructure, and in doing so, you must evaluate the existing access privileges your organization employs on a routine basis.
In this article, we will learn the importance of adding Identity Context to RADIUS authentication when planning the security architecture for your organization.
What is ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Architecture)?
As the name suggests, ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Architecture) implies a network infrastructure in which access privileges are granted by following zero trust policies. In ZTNA, users or devices are given the least privilege necessary to access the network resources needed to fulfill their role.
In a typical network architecture, a user that requests access is first authorized as a valid user, then authenticated to the network. They can “move” about freely within the network, accessing any resources hosted there, such as shared files or payroll information.
An essential tenet of ZTNA is defense in depth – or multiple layers of redundant defenses. A zero trust approach to the authentication event described above would have the user authorize again for each resource they access. The goal of defense in depth is to mitigate the damage caused by penetration – even if they manage to authorize the network, they would need to have appropriate credentials to authorize the payroll software.
Role of Attributes in ZTNA
Attributes are the building blocks of the policies, and diverse policies play a significant role in enhancing the “access control” within an enterprise.
Many organizations have used traditional access control policies like RBAC (Role Based Access Control) in the past to customize the access of resources to designated users based on their assigned roles, but ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control) has empowered these organizations to practice more granular control over their resources.
With its multidimensional attributes, ABAC has strengthened the traditional access control models, especially for organizations that can not afford to compromise their security and are more vulnerable owing to their size and exposure.
ABAC has been a vital tool in achieving Zero Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA) within an organization because it defines a model for network access based on user or device attributes. It enables smarter access policies that help your network identify and flag suspicious activity or prevent it outright.
For example, while using attributes in ABAC, an organization can define policies based on many characteristics, such as location, time zones, and designation, apart from the traditional attributes, such as name and email-id. This enables the organization to provide multi-layered security in ZTNA, which was difficult using traditional attributes.
ABAC also enables micro-segmentation in a Zero Trust atmosphere, and we at Securew2 play a prominent role in allowing ZTNA for our customers by segmenting the network and identifying all the reliable network connections.
Context-Based Identity Management
Identity is the new backbone for conditional access and is fundamental for zero-trust network architecture. Identity serves as the foundation for zero trust and is the best solution to manage secure connectivity to apps, data, and other resources in a contemporary business.
Over time, the context has become a new approach through which identity becomes increasingly relevant in evaluating risk management, malware detection, and enterprise integration as identity management evolves.
Context-Based Identity Management is a security concept that assists organizations in overcoming the rising security threat by employing conditional access policies and authorization features in the organization’s database. It takes into account both the traditional access control techniques like RBAC as well the dynamic access control techniques like ABAC in a ZTNA framework.
How Context-Based Identity Management Works
Context-based identity management is an automated feature of authentication and authorization that enables you to gather contextual information whenever a user logs onto your network. These Contextual data and information are obtained instantly by using various dynamic attributes such as:
- Location
- IP Address
- Device History
- Personal Information
- Gender
- Age
- Behavior
These attributes usually enhance the security of the organization by validating the users’ identities more precisely before authenticating and authorizing them access. For instance, If a user attempts to access the system through a public Wi-Fi network instead of their office or home network, access may be refused if this is not consistent with the user’s usual behavior.
Adding Identity Context to RADIUS Authentication
We at SecureW2 have been enhancing RADIUS authentication with identity context since our inception through the use of X.509 digital certificates.
SecureW2’s Managed PKI automatically configures and enrolls managed company-owned devices through our managed device gateway APIs. You don’t have to worry about the complexities involved in the setup because, as the name suggests, it’s fully managed. In the EKU (Extended Key Usage) section of the certificate template, we also provide the specific purpose of the certificate rather than issuing it randomly.
One of the most significant factors differentiating our Managed PKI service is that we can define multiple customizable policies based on identities that consider any number of attributes. We have policies described for each step, from authentication and enrollment to the lookup, that have vastly contributed to improving access control rules.
Our policies allow admins to configure several security policies and set up a Cloud RADIUS server that dynamically authorizes users and devices into custom security groups.
An ideal RADIUS deployment plan involves connecting with your identity provider to look up a user/device during the RADIUS authentication process. The RADIUS server then dynamically assigns the user to the appropriate security group based on your custom settings.
Simplify Identity Context with Cloud RADIUS
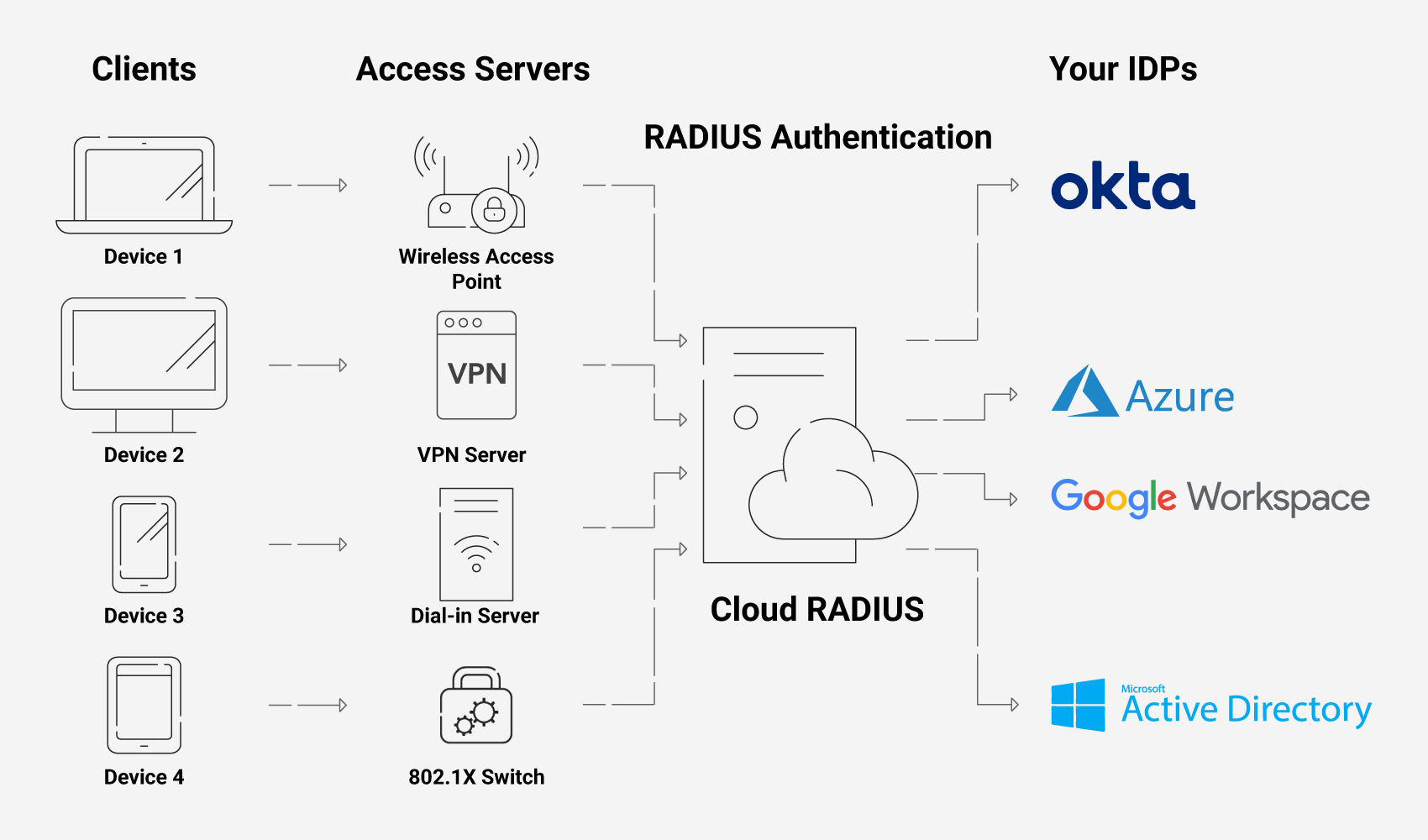
Our Cloud RADIUS enables advanced Identity Context using diverse attributes that can be easily customized to suit the needs of any organization. It also has built-in redundancy for load balancing and to ensure uptime in the event of outages or disasters.
Also, our Cloud RADIUS is vendor-neutral and compatible with almost all cloud-based IDPs, such as Azure/Okta/Google, that can securely authenticate remote users. We also have an experienced support team that is always available to assist you in configuring a RADIUS server in a matter of minutes, and they have excellent expertise in what they do.
You can book a call with us or check out our pricing page to see if SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS solutions fit the authentication needs of your organization.