5 Cyberattacks Mitigated by 802.1X Wi-Fi
The complexity and severity of cyberattacks are rising, leading to potential ramifications such as compromised data security, monetary deficits, and harm to a firm’s reputation.
Cyberattacks may manifest in multiple routes, from malicious software and computer viruses to phishing scams. A significant risk is hackers attacking the Wi-Fi networks and stealing sensitive data gained via unauthorized access. Hence it becomes imperative to take precautions against future cyberattacks.
Implementing the 802.1X Wi-Fi security protocol is a viable and secure route to cease the risk of invasion to your cyber networking. Enterprises widely utilize the protocol in question because it bolsters network security. Are you aware of the potentially disastrous implications that cyberattacks can have? We’ll discuss the five most prevalent cyberattacks, their impact, and how 802.1X can help eliminate those risks.
Five Types of Cyberattacks and Their Impact on Network Security
There exist various prevalent categories of Wi-Fi cyberattacks, which encompass:
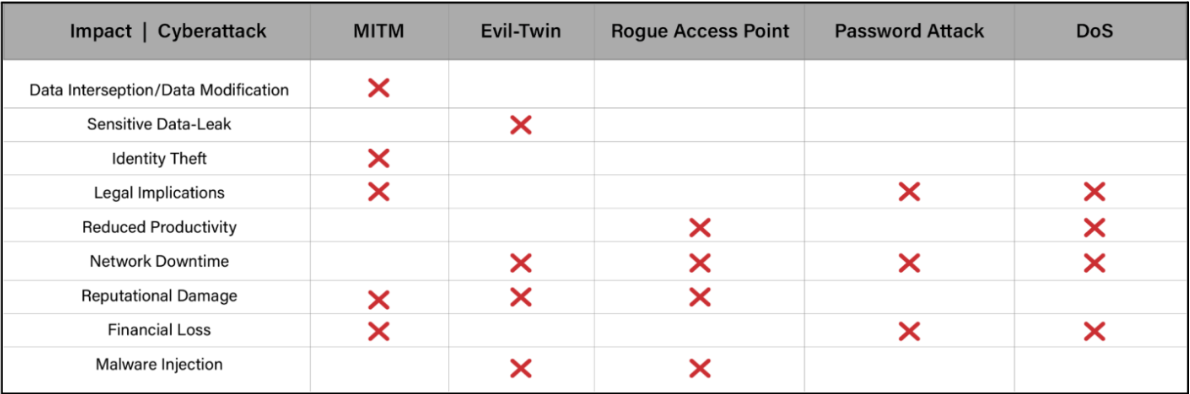
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack is a method attackers use to thwart, eavesdrop, exfiltrate data, or insert malicious code into the communication path between two devices.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack is an attacker’s attempt to bombard a network with excessive data, resulting in authorized users getting denied access to network resources.
- Rogue Access Point Attack involves setting up a legitimate fake access point, allowing the attacker to intercept data or steal login credentials.
- Password Attack involves an attacker who may try to guess or crack Wi-Fi passwords to obtain illegal access to a Wi-Fi network.
- Evil Twin Attack involves establishing a phony access point with the same name as a legitimate one, causing users to connect inadvertently to the fake network and allowing the perpetrator to intercept data or capture login credentials.
Impact of Cyber Attacks
The effect of cyberattacks can be brutal, and different types of such attacks lead to various repercussions. Let’s analyze some potential effects of different types of cyberattacks:
802.1X Wi-Fi
How Does 802.1X Wi-Fi Authentication Work?
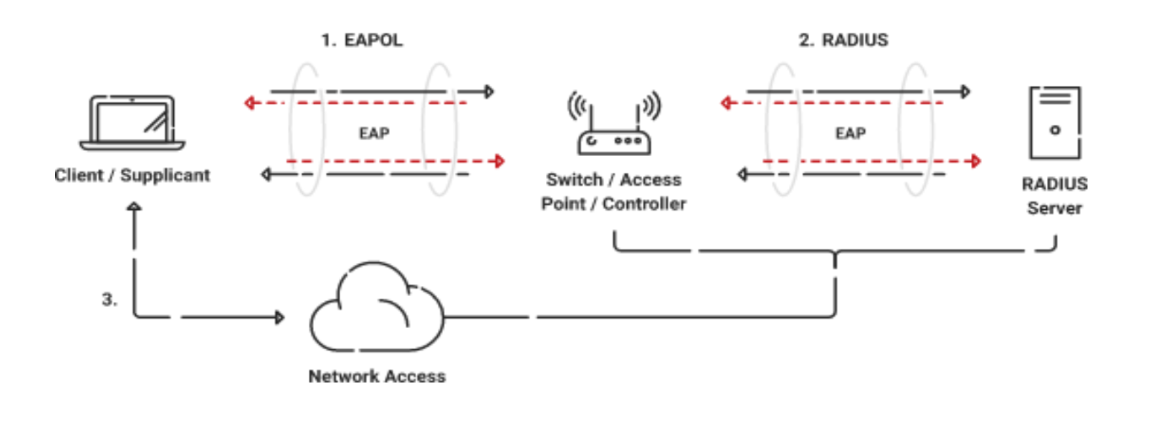
The 802.1X Wi-Fi authentication procedure involves three essential components: the supplicant, the authenticator, and the authentication server. A device seeking access to a network is referred to as the supplicant, which could be a laptop, smartphone, or tablet. The wireless access point (WAP) authenticator oversees the web access, whereas an authentication server validates the supplicant’s identity.
The authentication process can be outlined as follows:
- The supplicant initiates the 802.1X authentication by transmitting an EAPOL-Start message to the authenticator, requesting network access.
- The authenticator verifies the identity via the supplicant, which contains the credentials (e.g., a username and password).
- Then, the authenticator relays these credentials to the authentication server for verification and responds back to the authenticator.
- The authenticator then allows the supplicant to access the network. However, access will be denied if access control policies are not met.
- Implementing the 802.1X Wi-Fi protocol enforces authentication before network access, ensuring that only approved users are granted access to the network. This measure is essential in mitigating security threats and preventing unauthorized access.
Gain insight into the intricacies of 802.1X Wi-Fi authentication by delving into the technical minutiae provided at this link.
Using 802.1X Wi-Fi
Step into the world of 802.1X authentication! This high-tech process consists of four crucial steps: authentication, encryption, access control, and monitoring. First, let’s explore the benefits of each stage.
1. Authentication: The first layer of protection offered by 802.1X is authentication. Only verified users are granted access to the network, limiting the potential target pool for cybercriminals.
2. Encryption: Encryption is operated by 802.1X to guard data during communication over the network; this implies that even if an attacker manages to intercept the data, they cannot decipher it.
3. Access control: The access control may be used by administrators to set up 802.1X based on user ID, device kind, and physical location.
4. Monitoring: 802.1X enables the admins to spot and respond to any threats in real time with the help of real-time network monitoring.
How Does 802.1X Provide Security Against Cyberattacks?
Let’s see how implementing 802.1X can be leveraged to address the various cyberattacks.
MITM Attacks: 802.1X enforces mutual authentication to eliminate the potential of man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. When the client establishes the connection to the network, the access point triggers a certificate exchange to authenticate its identity. Subsequently, the client transmits its certificate to the access point (AP) for the purpose of identity authentication. The implementation of mutual authentication guarantees that the client device establishes a connection with the exact access point, thereby preventing any unauthorized access by potential attackers.
Rogue Access Points: 802.1X protocol can help determine any rogue access points (APs) on the network. The APs request information from the authentication server to confirm the client’s credentials when the client establishes a connection to the network. If an Access Point (AP) receives a response from an unknown server, it is possible to infer the existence of a rogue AP within the network.
Password Attacks: It’s worth noting that the 802.1X authentication mechanism doesn’t rely on passwords making it unsusceptible to password attacks. Rather than relying on traditional authentication methods, it leverages digital certificates and other techniques to ensure secure authentication.
Denial-of-Service (DoS): Implementing 802.1X can effectively mitigate DoS attacks by restricting the volume of client requests. In the event of excessive authentication requests from a client, the access point can reject any additional requests.
Evil Twin: The 802.1X protocol is impervious to evil twin attacks as it employs digital certificates for authentication. The certificates in question are non-replicable, preventing potential attackers from forging an AP that authorizes clients through these certificates.
A Comparative Analysis of the 802.1X Wi-Fi With Other Protocols
Implementing the 802.1X protocol mandates the authentication of users using login credentials before granting network access. It boasts higher security than other Wi-Fi security protocols like WEP and WPA, which utilize a shared key for access. Here are several comparative analyses:
802.1X vs. WEP: WEP is an outdated and insecure encryption standard. It offers no security beyond basic encryption methods and may be susceptible to hacker efforts. 802.1X is a more sophisticated protocol that provides more safety. In addition, it can be set up to accommodate various gadgets and user profiles, and it employs authentication to control access. Therefore, 802.1X is preferable if you want reliable security for your wireless network.
802.1X vs. WPA: The 802.1X protocol is an authentication mechanism restricting network access to only users with valid credentials, which are requested and verified before granting access. On the other hand, WPA ensures the protection of data transmission through encryption when utilizing unsecured wireless networks. Both protocols offer security measures. However, they fulfill particular purposes. Furthermore, the 802.1X protocol facilitates mutual authentication between the user and the device, while WPA ensures the confidentiality of data during transmission via encryption.
802.1X vs. MAC filtering: While both 802.1X and MAC filtering serve to restrict network access, they do this in distinct ways. 802.1X is a more secure protocol for user authentication via usernames, passwords, or other identifying information before network access.
A device’s MAC address determines whether it may join a network. MAC filtering may be more secure than 802.1X since attackers can falsify MAC addresses and get network access. For less secure networks, MAC filtering may suffice. 802.1X detects malicious APs. The AP asks for authentication server verification when a client connects to the network. An unknown server answer indicates a rogue AP on the web.
Would you like to determine the optimal encryption protocol for your wireless network? Please navigate to this page for further information.
Role of SecureW2 in Implementing 802.1X Wi-Fi
Are you tired of worrying about your organization’s cybersecurity? Stop stressing and start securing with SecureW2. Our innovative solutions provide the protection and peace of mind your business needs.
With SecureW2’s turnkey solution, you can upgrade your existing infrastructure as we will fill in the current gaps. We provide a scalable and user-friendly solution that simplifies the implementation of 802.1X and certificates across organizations of any size. In addition, it renders a streamlined authentication, authorization, and accounting (i.e., Cloud RADIUS) process, forming the basis for network security.
SecureW2 facilitates the installation of secure and centralized Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and Certificate Authority (CA) services. This solution boosts seamless administration and provision of digital certificates for all network endpoints, engulfing Bring-Your-Own-Device (BYOD) and Internet of Things (IoT) endpoints, via a comprehensive automation of the certificate lifecycle workflow.
Don’t let hackers have the upper hand. Instead, take control of your organization’s cybersecurity with us. Our cutting-edge technology and unmatched assistance from our experts will ensure the safety and security of your data. Kickstart your journey by clicking here.